
1. 协调器工作流程图
- 上面一张图选自langGraph
- 下面一张选自SpingAI


2. 适用场景
- 适用于对无法预测所需子任务的复杂任务
- 在拓扑结构与并行化类似,但更比并行化更灵活
- 子任务并非预先定义,由协调器(编排器)输入而定
3. 代码示例
3.1 启动部分(入口)
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder){
var chatClient = chatClientBuilder.build();
return args -> {
new OrchestratorWorkers(chatClient).process("给依依介绍一下富婆对象");
};
}
}
3.2 协调器部分
3.2.1 协调器部分提示词
public static final String DEFAULT_ORCHESTRATOR_PROMPT = """
分析这项任务,并将其分解为2-3种不同的方法:
任务: {task}
以JSON格式返回
\\{
"analysis": "解释你对任务的理解,以及哪些变化是有价值的。关注每种方法如何服务于任务的不同方面。",
"tasks": [
\\{
"type": "formal",
"description": "写一个精确的技术版本,强调规格"
\\},
\\{
"type": "conversational",
"description": "写一个吸引人、友好的版本,与读者建立联系"
\\}
]
\\}
""";
3.2.2 协调器部分代码
- 协调器部分,先拆分任务意图
- OrchestratorResponse 实体返回则是意图与多个子任务
OrchestratorResponse orchestratorResponse = this.chatClient.prompt()
.user(u -> u.text(this.orchestratorPrompt).param("task", taskDescription))
.call().entity(OrchestratorResponse.class);
public static record OrchestratorResponse(String analysis, List<Task> tasks) {
}
3.3 work部分
3.3.1 work提示词
public static final String DEFAULT_WORKER_PROMPT = """
生成的内容如下:
任务: {original_task}
风格: {task_type}
指向: {task_description}
""";
3.3.2 work工作流
List<String> workerResponses = orchestratorResponse.tasks()
.stream()
.map(task -> this.chatClient.prompt()
.user(u -> u.text(this.workerPrompt)
.param("original_task", taskDescription)
.param("task_type", task.type())
.param("task_description", task.description()))
.call().content()).toList();
3.3.3 FinalResopnse汇总
public static record FinalResponse(String analysis, List<String> workerResponses) {
}
return new FinalResponse(orchestratorResponse.analysis(), workerResponses);
3.3.4 完整的OrchestratorWorkers
package com.coderpwh.work;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import java.util.List;
public class OrchestratorWorkers {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
private final String orchestratorPrompt;
private final String workerPrompt;
public static final String DEFAULT_ORCHESTRATOR_PROMPT = """
分析这项任务,并将其分解为2-3种不同的方法:
任务: {task}
以JSON格式返回
\\{
"analysis": "解释你对任务的理解,以及哪些变化是有价值的。关注每种方法如何服务于任务的不同方面。",
"tasks": [
\\{
"type": "formal",
"description": "写一个精确的技术版本,强调规格"
\\},
\\{
"type": "conversational",
"description": "写一个吸引人、友好的版本,与读者建立联系"
\\}
]
\\}
""";
public static final String DEFAULT_WORKER_PROMPT = """
生成的内容如下:
任务: {original_task}
风格: {task_type}
指向: {task_description}
""";
public static record Task(String type, String description) {
}
public static record OrchestratorResponse(String analysis, List<Task> tasks) {
}
public static record FinalResponse(String analysis, List<String> workerResponses) {
}
public OrchestratorWorkers(ChatClient chatClient) {
this(chatClient, DEFAULT_ORCHESTRATOR_PROMPT, DEFAULT_WORKER_PROMPT);
}
public OrchestratorWorkers(ChatClient chatClient, String orchestratorPrompt, String workerPrompt) {
Assert.notNull(chatClient, "ChatClient must not be null");
Assert.notNull(orchestratorPrompt, "Orchestrator prompt must not be null");
Assert.notNull(workerPrompt, "Worker prompt must not be null");
this.chatClient = chatClient;
this.orchestratorPrompt = orchestratorPrompt;
this.workerPrompt = workerPrompt;
}
@SuppressWarnings("null")
public FinalResponse process(String taskDescription) {
Assert.hasText(taskDescription, "Task description must not be empty");
OrchestratorResponse orchestratorResponse = this.chatClient.prompt()
.user(u -> u.text(this.orchestratorPrompt).param("task", taskDescription))
.call().entity(OrchestratorResponse.class);
System.out.println(String.format("\n=== ORCHESTRATOR OUTPUT ===\n分析: %s\n\n任务: %s\n",
orchestratorResponse.analysis(), orchestratorResponse.tasks()));
List<String> workerResponses = orchestratorResponse.tasks()
.stream()
.map(task -> this.chatClient.prompt()
.user(u -> u.text(this.workerPrompt)
.param("original_task", taskDescription)
.param("task_type", task.type())
.param("task_description", task.description()))
.call().content()).toList();
System.out.println("\n=== WORKER OUTPUT ===\n" + workerResponses);
return new FinalResponse(orchestratorResponse.analysis(), workerResponses);
}
}
4. 应用实例
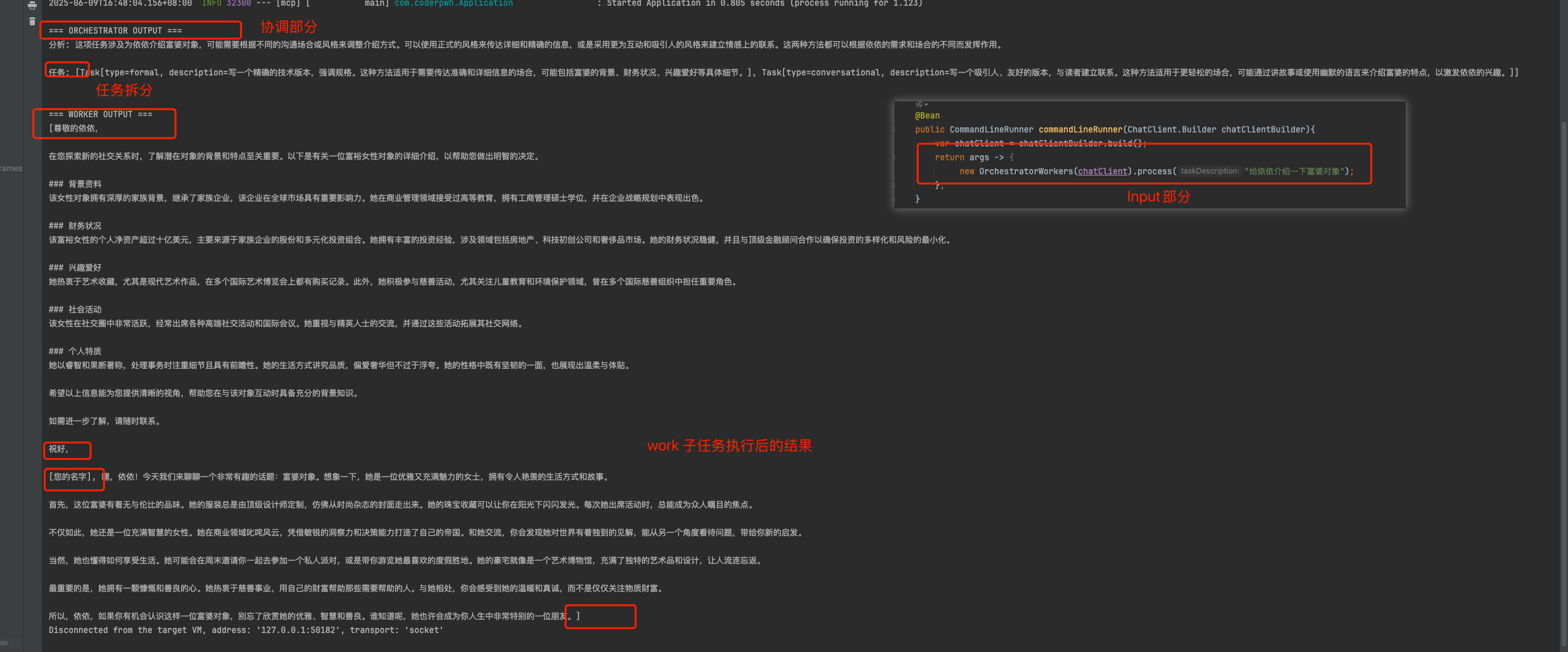
4.1 输入部分
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder){
var chatClient = chatClientBuilder.build();
return args -> {
new OrchestratorWorkers(chatClient).process("给依依介绍一下富婆对象");
};
}
4.2 提示词部分省略
4.3 输出部分
5. 归纳
- 协调器主要流程分文3步
- 通过协调器,分析其意图,拆分成多个子任务
- 对多个子任务进行执行
- 对协调器意图与子任务合并进行output





